Fermion

In particle physics, a fermion is a particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-odd-integer spin (spin 1/2, spin 3/2, etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics.
Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions.
In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referred to as the spin-statistics relation is, in fact, a spin statistics-quantum number relation.[1]
As a consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, only one fermion can occupy a particular quantum state at a given time. Suppose multiple fermions have the same spatial probability distribution. Then, at least one property of each fermion, such as its spin, must be different. Fermions are usually associated with matter, whereas bosons are generally force carrier particles. However, in the current state of particle physics, the distinction between the two concepts is unclear. Weakly interacting fermions can also display bosonic behavior under extreme conditions. For example, at low temperatures, fermions show superfluidity for uncharged particles and superconductivity for charged particles.
Composite fermions, such as protons and neutrons, are the key building blocks of everyday matter.
English theoretical physicist Paul Dirac coined the name fermion from the surname of Italian physicist Enrico Fermi.[2]
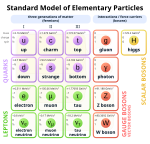
Elementary fermions
[edit]| Standard Model of particle physics |
|---|
 |
The Standard Model recognizes two types of elementary fermions: quarks and leptons. In all, the model distinguishes 24 different fermions. There are six quarks (up, down, strange, charm, bottom and top), and six leptons (electron, electron neutrino, muon, muon neutrino, tauon and tauon neutrino), along with the corresponding antiparticle of each of these.
Mathematically, there are many varieties of fermions, with the three most common types being:
- Weyl fermions (massless),
- Dirac fermions (massive), and
- Majorana fermions (each its own antiparticle).
Most Standard Model fermions are believed to be Dirac fermions, although it is unknown at this time whether the neutrinos are Dirac or Majorana fermions (or both). Dirac fermions can be treated as a combination of two Weyl fermions.[3]: 106 In July 2015, Weyl fermions have been experimentally realized in Weyl semimetals.
Composite fermions
[edit]Composite particles (such as hadrons, nuclei, and atoms) can be bosons or fermions depending on their constituents. More precisely, because of the relation between spin and statistics, a particle containing an odd number of fermions is itself a fermion. It will have half-integer spin.
Examples include the following:
- A baryon, such as the proton or neutron, contains three fermionic quarks.
- The nucleus of a carbon-13 atom contains six protons and seven neutrons.
- The atom helium-3 (3He) consists of two protons, one neutron, and two electrons. The deuterium atom consists of one proton, one neutron, and one electron.
The number of bosons within a composite particle made up of simple particles bound with a potential has no effect on whether it is a boson or a fermion.
Fermionic or bosonic behavior of a composite particle (or system) is only seen at large (compared to size of the system) distances. At proximity, where spatial structure begins to be important, a composite particle (or system) behaves according to its constituent makeup.
Fermions can exhibit bosonic behavior when they become loosely bound in pairs. This is the origin of superconductivity and the superfluidity of helium-3: in superconducting materials, electrons interact through the exchange of phonons, forming Cooper pairs, while in helium-3, Cooper pairs are formed via spin fluctuations.
The quasiparticles of the fractional quantum Hall effect are also known as composite fermions; they consist of electrons with an even number of quantized vortices attached to them.
See also
[edit]- Anyon, 2D quasiparticles
- Chirality (physics), left-handed and right-handed
- Fermionic condensate
- Weyl semimetal
- Fermionic field
- Identical particles
- Kogut–Susskind fermion, a type of lattice fermion
- Majorana fermion, each its own antiparticle
- Parastatistics
- Skyrmion, a hypothetical particle
Notes
[edit]- ^ Weiner, Richard M. (4 March 2013). "Spin-statistics-quantum number connection and supersymmetry". Physical Review D. 87 (5): 055003–05. arXiv:1302.0969. Bibcode:2013PhRvD..87e5003W. doi:10.1103/physrevd.87.055003. ISSN 1550-7998. S2CID 118571314. Retrieved 28 March 2022.
- ^ Notes on Dirac's lecture Developments in Atomic Theory at Le Palais de la Découverte, 6 December 1945, UKNATARCHI Dirac Papers BW83/2/257889. See note 64 on page 331 in "The Strangest Man: The Hidden Life of Paul Dirac, Mystic of the Atom" by Graham Farmelo
- ^ T. Morii; C. S. Lim; S. N. Mukherjee (1 January 2004). The Physics of the Standard Model and Beyond. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-279-560-1.