Whole-tone scale
| Qualities | |
|---|---|
| Number of pitch classes | 6 |
| Forte number | 6-35 |
| Complement | 6-35 |

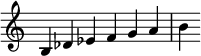
In music, a whole-tone scale is a scale in which each note is separated from its neighbors by the interval of a whole tone. In twelve-tone equal temperament, there are only two complementary whole-tone scales, both six-note or hexatonic scales. A single whole-tone scale can also be thought of as a "six-tone equal temperament".
The whole-tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, [and] the scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect".[2] This effect is especially emphasised by the fact that triads built on such scale tones are all augmented triads. Indeed, all six tones of a whole-tone scale can be played simply with two augmented triads whose roots are a major second apart. Since they are symmetrical, whole-tone scales do not give a strong impression of the tonic or tonality.
Only two triads are possible, both of them augmented, and...all inversions sound alike. All 'progressions' tend to have the same tonal character. What one hears are tone centers rather than tonics, and only when they are stressed [emphasized], as by repetition or duration. It cannot be denied that the small number of possible different intervals [only even semitone intervals: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10] and nonequivalent chords available in the whole-tone scale results in a soft-edged, neutral kind of sound lacking in tonal contrast.... Since the 1930s...whole-tone harmony...has become one of the platitudes of the "Hollywood Style."
The composer Olivier Messiaen called the whole-tone scale his first mode of limited transposition. The composer and music theorist George Perle calls the whole-tone scale interval cycle 2, or C2. Since there are only two possible whole-tone-scale positions (that is, the whole-tone scale can be transposed only once), it is either C20 or C21. For this reason, the whole-tone scale is also maximally even and may be considered a generated collection.
Due to this symmetry, the hexachord consisting of the whole-tone scale is not distinct under inversion or more than one transposition. Thus many composers have used one of the "almost whole-tone" hexachords, whose "individual structural differences can be seen to result only from a difference in the 'location', or placement, of a semitone within the otherwise whole-tone series."[4] Alexander Scriabin's mystic chord is a primary example, being a whole-tone scale with one note raised a semitone; this alteration allows for a greater variety of resources through transposition.[5]
Classical music
[edit]In 1662, Johann Rudolf Ahle wrote a melody to the lyrics of Franz Joachim Burmeister's "Es ist genug" (It is enough), beginning it with four notes of the whole-tone scale on the four syllables.[clarification needed] Johann Sebastian Bach chose the chorale to end his cantata O Ewigkeit, du Donnerwort, BWV 60, set for four parts. The first four measures are shown below.
Mozart also used the scale in his Musical Joke, for strings and horns.[6]

In the 19th century, Russian composers went further with melodic and harmonic possibilities of the scale, often to depict the ominous; examples include the endings of the overtures to Glinka's opera Ruslan and Lyudmila and Borodin's Prince Igor, and the Commander's theme in Dargomyzhsky's The Stone Guest. Further examples can be found in the works of Rimsky-Korsakov: the sea king's music in Sadko and also in Scheherazade. Shown below is the opening theme to Scheherazade, which is "simply a descending whole-tone scale with diatonic trimmings."[8] Notes in the whole-tone scale are highlighted.
(For some short piano pieces written completely in whole-tone scale, see Nos. 1, 6, and 7 from V.A. Rebikov's Празднество (Une fête), Op. 38, from 1907.)
H. C. Colles names as the "childhood of the whole-tone scale" the music of Berlioz and Schubert in France and Austria and then Russians Glinka and Dargomyzhsky.[9] Claude Debussy, who had been influenced by Russians, along with other impressionist composes made extensive use of whole-tone scales. Voiles, the second piece in Debussy's first book of Préludes, is almost entirely within one whole-tone scale.[10][11] The opening measures are shown below.
Janáček's use of the scale in the bracing opening to the second movement of his Sinfonietta is, to quote William W. Austin, "utterly different". Austin writes, "Janáček’s free chromaticism never loses touch with a diatonic scale for long. Though the whole-tone scale is prominent in much of his music after 1905 when he encountered Debussy, it serves simply to fit the motifs over augmented chords. The same motifs return from the whole-tone to the diatonic scale without emphasizing the contrast."[12] The first measures of the second movement of Sinfonietta are shown below.

Giacomo Puccini used whole-tone scales as well as pentatonic scales in his 1904 opera Madama Butterfly to imitate east Asian music styles.
The first of Alban Berg's Seven Early Songs opens with a whole-tone passage both in the orchestral accompaniment and in the vocal line that enters a bar later.[13] Berg also quotes the Bach chorale setting referred to above in his Violin Concerto. The last four notes of the 12-tone row Berg used are B, C♯, E♭ and F, which, together with the first note, G, comprise five of the six notes of the scale.)
Béla Bartók also uses whole-tone scales in his fifth string quartet.[14] Ferruccio Busoni used the whole-tone scale in the right hand part of the "Preludietto, Fughetta ed Esercizio" of his An die Jugend, and Franz Liszt had used the technique as early as 1831, in the Grande Fantaisie sur La clochette.[15]
Jazz
[edit]Some early instances of the use of the scale in jazz writing can be found in Bix Beiderbecke's "In a Mist" (1928) and Don Redman’s "Chant of the Weed" (1931). In 1958, Gil Evans recorded an arrangement that gives striking coloration to the "abrupt whole-tone lines"[16] of Redman's original. Wayne Shorter's composition "JuJu" (1965),[17] features heavy use of the whole-tone scale, and John Coltrane's "One Down, One Up" (1965), is built on two augmented chords arranged in the same simple structure as his earlier tune "Impressions".[18]
However, these are only the most overt examples of the use of this scale in jazz. A vast number of jazz tunes, including many standards, use augmented chords and their corresponding scales as well, usually to create tension in turnarounds or as a substitute for a dominant seventh chord. For instance a G7 augmented 5th dominant chord in which G altered scale tones would work before resolving to C7, a tritone substitution chord such as D♭9 or D♭7♯11 is often used in which D♭/G whole-tone scale tones will work, the sharpened 11th degree being a G and the flattened 7th being a C♭, the enharmonic equivalent of B, the major third in the G dominant chord.
Art Tatum and Thelonious Monk are two pianists who used the whole-tone scale extensively and creatively. Monk's "Four in One" (1948)[19] and "Trinkle-Tinkle" (1952)[20] are fine examples of this.
A prominent example of the whole-tone scale that made its way into pop music are bars two and four of the opening of Stevie Wonder's 1972 song "You Are the Sunshine of My Life".[21]
Non-Western music
[edit]The raga Sahera in Hindustani classical music uses the same intervals as the whole-tone scale. Ustad Mehdi Hassan has performed this rāga.[citation needed] Gopriya is the corresponding Carnatic rāgam.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Piston, Walter (1987/1941). Harmony, p. 490. 5th edition revised by Devoto, Mark. W. W. Norton, New York/London. ISBN 0-393-95480-3.
- ^ Kamien, Roger (2008). Music: An Appreciation, Sixth Brief Edition, p.308. ISBN 978-0-07-340134-8.
- ^ Piston (1987/1941), p. 492.
- ^ Schmalfeldt, Janet (1983). Berg's Wozzeck: Harmonic Language and Dramatic Design, p.48. ISBN 0-300-02710-9.
- ^ "The Evolution of Twelve-Note Music", p. 56. Oliver Neighbor. Proceedings of the Royal Musical Association, 81st session (1954–1955), pp. 49–61.
- ^ Rosen, Charles (January 1995). The Romantic Generation. Cambridge, Mass. pp. 556. ISBN 0674779339. OCLC 31710528.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Piston (1987/1941), p. 491. Piston analyses viio7 as Vo
9 (with a missing/implied root) and doesn't include macro analysis. - ^ Abraham, Gerald. "The Whole-Tone Scale in Russian Music", p. 602, The Musical Times, vol. 74, no. 1085. (July 1933), pp. 602–604.
- ^ "The Childhood of the Whole-Tone Scale", pp. 17-19. H. C. Colles. The Musical Times, vol. 55, no. 851. (January 1, 1914), pp. 16–20.
- ^ Benward & Saker (2009). Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II, p. 246. Eighth edition. ISBN 978-0-07-310188-0.
- ^ Benward & Saker (2003). Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I, p. 39. Seventh edition. ISBN 978-0-07-294262-0.
- ^ Austin, William W. (1966). Music in the 20th Century: From Debussy through Stravinsky. New York: W. W. Norton. p. 81. ISBN 0393097048. OCLC 504195.
- ^ Berg (1928), Sieben Fruhe Lieder, Wien, Universal Edition
- ^ Cooper, David (1996). Bartók: Concerto for Orchestra. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 70. ISBN 0521480043. OCLC 32626039.
- ^ Jeremy Nicholas, "Loving Liszt", Limelight, April 2011, p. 50
- ^ Harrison, Max (1960) "Gil Evans: the Arranger as re-composer", article in Jazz Monthly, February.
- ^ Wayne Shorter Jazz Play Along, Milwaukee, Hal Leonard
- ^ Impressions (sheet music, 1991) from The Music of John Coltrane, Milwaukee, Hal Leonard
- ^ Four in One from Cardenas, S. and Sickler, D. (eds.) Thelonious Monk Fakebook, Milwaukee, Hal Leonard.
- ^ "Trinkle-Tinkle" from Cardenas, S. and Sickler, D. (eds.) Thelonious Monk Fakebook, Milwaukee, Hal Leonard.
- ^ Everett, Walter (2008). The Foundations of Rock : From "Blue Suede Shoes" to "Suite: Judy Blue Eyes". Oxford University Press. p. 174. ISBN 9780199718702.


![\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff <<
\new Voice \relative c' {
\stemUp \clef treble \key f \major \time 4/4
\[ f2 g4 a
b2 \] r4 b
c4 g g bes!
a2.
}
\new Voice \relative c' {
\stemDown
c2 c4 bes8 a
e'2 s4 e
e4. f8 e d e c
f2.
}
>>
\new Staff <<
\new Voice \relative c' {
\stemUp \clef bass \key f \major \time 4/4
a2 g4 d'
d2 r4 gis,
a8 b c4 c c
c2.
}
\new Voice \relative c {
\stemDown
f2 e4 fis
gis2 s4 e
a8 g!16 f e8 d c bes! a g!
f2.
}
>>
>>](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/8/3/833ctj78p61r0nisuerg7hiw19l273v/833ctj78.png)

