Bone marrow examination
| Bone marrow examination | |
|---|---|
 | |
| MeSH | D001856 |
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself (drawn from a vein by phlebotomy), it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
Components of the procedure
[edit]
Bone marrow samples can be obtained by aspiration and trephine biopsy. Sometimes, a bone marrow examination will include both an aspirate and a biopsy. The aspirate yields semi-liquid bone marrow, which can be examined by a pathologist under a light microscope and analyzed by flow cytometry, chromosome analysis, or polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Frequently, a trephine biopsy is also obtained, which yields a narrow, cylindrically shaped solid piece of bone marrow, 2 mm wide and 2 cm long (80 μL), which is examined microscopically (sometimes with the aid of immunohistochemistry) for cellularity and infiltrative processes. An aspiration, using a 20 mL syringe, yields approximately 300 μL of bone marrow.[1] A volume greater than 300 μL is not recommended, since it may dilute the sample with peripheral blood.[1]
| Aspiration | Biopsy | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Drawbacks | Does not represent all cells | Slow processing |
Aspiration does not always represent all cells since some such as lymphoma stick to the trabecula, and would thus be missed by a simple aspiration.[citation needed]
Site of procedure
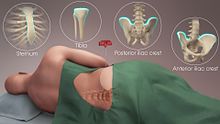
[edit]Bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy are usually performed on the back of the hipbone, or posterior iliac crest. An aspirate can also be obtained from the sternum (breastbone). For the sternal aspirate, the patient lies on their back, with a pillow under the shoulder to raise the chest. A trephine biopsy should never be performed on the sternum, due to the risk of injury to blood vessels, lungs or the heart. Bone marrow aspiration may also be performed on the tibial (shinbone) site in children up to 2 years of age while spinous process aspiration is frequently done in a lumbar puncture position and on the L3-L4 vertebrae.[citation needed]
Anesthesia is used to reduce surface pain at the spot where the needle is inserted. Pain may result from the procedure's insult to the marrow, which cannot be anesthetized, as well as short periods of pain from the anesthetic process itself. The experience is not uniform; different patients report different levels of pain, and some do not report any pain at certain expected points.[2]
Test performance
[edit]
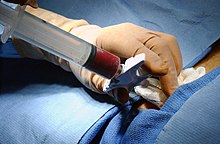
A bone marrow biopsy may be done in a health care provider's office or in a hospital. Informed consent for the procedure is typically required. The patient is asked to lie on their abdomen (prone position) or on their side (lateral decubitus position). The skin is cleansed, and a local anesthetic such as lidocaine or procaine is injected to numb the area. Patients may also be pretreated with analgesics and/or anti-anxiety medications, although this is not a routine practice.
Typically, the aspirate is performed first. An aspirate needle is inserted through the skin using manual pressure and force until it hits the bone. Then, with a twisting motion of clinician's hand and wrist, the needle is advanced through the bony cortex (the hard outer layer of the bone) and into the marrow cavity. Once the needle is in the marrow cavity, a syringe is attached and used to aspirate ("suck out") liquid bone marrow. A twisting motion is performed during the aspiration to avoid excess content of blood in the sample, which might be the case if an excessively large sample from one single point is taken. Subsequently, the biopsy is performed if indicated. A different, larger trephine needle is inserted and anchored in the bony cortex. The needle is then advanced with a twisting motion and rotated to obtain a solid piece of bone marrow. This piece is then removed along with the needle. The entire procedure, once preparation is complete, typically takes 10–15 minutes.
If several samples are taken, the needle is removed between the samples to avoid blood coagulation.
After the procedure is complete, the patient is typically asked to lie flat for 5–10 minutes to provide pressure over the procedure site. After that, assuming no bleeding is observed, the patient can get up and go about their normal activities. Paracetamol (aka acetaminophen) or other simple analgesics can be used to ease soreness, which is common for 2–3 days after the procedure. Any worsening pain, redness, fever, bleeding or swelling may suggest a complication. Patients are also advised to avoid washing the procedure site for at least 24 hours after the procedure is completed.
Contraindications
[edit]
There are few contraindications to bone marrow examination. It is important to note that thrombocytopenia or bleeding disorders are not contraindications as long as the procedure is performed by a skilled clinician.[3] Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy can be safely performed even in the setting of extreme thrombocytopenia (low platelet count). If there is a skin or soft tissue infection over the hip, a different site should be chosen for bone marrow examination.[citation needed]
Complications
[edit]While mild soreness lasting 12–24 hours is common after a bone marrow examination, serious complications are extremely rare. In a large review, an estimated 55,000 bone marrow examinations were performed, with 26 serious adverse events (0.05%), including one fatality.[4] The same author collected data on over 19,000 bone marrow examinations performed in the United Kingdom in 2003, and found 16 adverse events (0.08% of total procedures), the most common of which was bleeding. In this report, complications, while rare, were serious in individual cases.[5]
Reference ranges for white blood cells in bone marrow
[edit]| Range (%)[6] | Reference range (%)[6] | Median (%)[6] | Mean (%)[6] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythroblasts (total) | 8.5–56.5 | 15.8–46.2 | 32 | 31.7 |
| Male | 11.0–54.5 | 16.2–46.6 | 33 | 32.4 |
| Female | 8.5–56.5 | 15.6–45.0 | 29.5 | 30.1 |
| Proerythroblast | 0–5.0 | 0–3.0 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Basophilic | 0–21.0 | 0.5–13.5 | 3.5 | 4.5 |
| Polychromatophilic | 3.0–47.0 | 7.8–34.5 | 20 | 20.2 |
| Orthochromatic | 0–21.0 | 0.5–16.5 | 5.5 | 6.3 |
| Granulocytes (total) | 24.5–72.5 | 34.8–66.3 | 49.5 | 49.9 |
| Male | 26.0–70.5 | 35.5–64.5 | 49.5 | 49.7 |
| Female | 24.5–72.5 | 34.1–67.4 | 50 | 50.5 |
| Neutrophils (total) | ||||
| Myeloblast | 0–8.5 | 0–5.0 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| Promyelocyte | 0–8.5 | 0–5.5 | 1 | 1.3 |
| Myelocyte | 1.0–31.7 | 5.8–24.0 | 13.5 | 13.7 |
| Metamyelocyte | 0.5–18.0 | 1.0–12.0 | 4.5 | 5 |
| Band | 2.0–34.0 | 6.5–26.2 | 14.5 | 15.2 |
| Segmented | 1.0–27.5 | 2.5–19.7 | 9.5 | 9.8 |
| Eosinophils (total) | 0–18.0 | 0.5–7.0 | 2.5 | 3 |
| Basophils (and mast cells) | 0–3.0 | 0–1.5 | 0 | 0.3 |
| GE-ratio | 0.5–5.9 | 0.8–4.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| Monocytes | 0–8.5 | 0–6.0 | 2 | 2.2 |
| ME ratio | 0.6–6.2 | 0.8–4.1 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| Male | 0.6–6.1 | 0.8–4.0 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| Female | 0.6–6.2 | 0.8–4.2 | 1.7 | 2 |
| Lymphocytes | 1.0–38.5 | 5.5–23.2 | 13.2 | 13.6 |
| Plasma cells | 0–17.5 | 0–7.0 | 2.3 | 2.6 |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b eMedicine "Specialties > Hematology > Diagnostic Procedures > Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy". Article last updated April 7, 2008.
- ^ What to Expect During a Bone Marrow Aspirate and Biopsy Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, n.d. Accessed 2014-08-08.
- ^ Malempati, Suman; Joshi, Sarita; Lai, Susanna; Braner, Dana A.V.; Tegtmeyer, Ken (2009). "Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy". New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (15): e28. doi:10.1056/NEJMvcm0804634. PMID 19812396.
- ^ Bain BJ (2003). "Bone marrow biopsy morbidity and mortality". Br. J. Haematol. 121 (6): 949–51. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04329.x. PMID 12786808.
- ^ Bain BJ (2005). "Bone marrow biopsy morbidity: review of 2003". J. Clin. Pathol. 58 (4): 406–8. doi:10.1136/jcp.2004.022178. PMC 1770618. PMID 15790706.
- ^ a b c d Parmentier S, Kramer M, Weller S, Schuler U, Ordemann R, Rall G; et al. (2020). "Reevaluation of reference values for bone marrow differential counts in 236 healthy bone marrow donors". Ann Hematol. 99 (12): 2723–2729. doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04255-4. PMC 7683448. PMID 32935189.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license
